Schooling (Under Age)
High Standard of Learning
In general, school education is 13 years and divided into:
1. Primary school
Runs for 7 or 8 years, starting at kindergarten/preparatory (early childhood education) through to Year 6 or 7.
2. Secondary school
Runs for 3 or 4 years, from Years 7 to 10 or 8 to 10.
3. Senior secondary school
Runs for 2 years, Years 11 and 12.
Early childhood education such as kindergarten/preparatory is intended to provide care and supervision of children, to prepare children for school, and to ensure that children are able to effectively participate in subsequent learning opportunities. Early childhood education is usually conducted in association with community programs, pre-schools and other child-care settings.
In Australia, it is compulsory for children to attend primary and secondary school education between the ages of 6 and 16 (Year 1 to Year 9 or 10). Primary and secondary education focus on developing essential literacy, numeracy and social skills, and provide foundational knowledge to children about the world around them.
Students who complete their senior secondary school program at Year 12 or equivalent are awarded a Senior Secondary Certificate of Education. They then leave school to undertake vocational or higher education courses and/or start work.
Key Statistics about School in Australia
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (2019):
For more information, please check Visit Source
- there were 3,948,811 students enrolled in 9,503 schools.
- teachers made up 68.5% of in-school full-time equivalent staff.
- the year 7 to 12 full-time apparent retention rate was 84.0%.
- the average student to teaching staff ratio for all schools was 13.7.
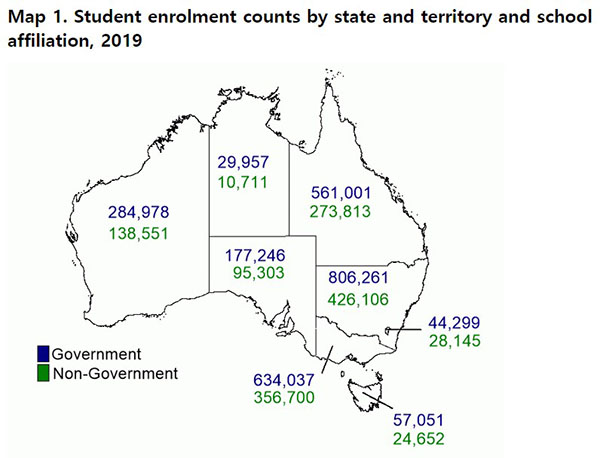
The map below shows the student enrolment counts by state and
territory and school affiliation in 2019:
Benefits of Schooling in Australia
Australian schools do not just educate students academically. Instead, they also prepare them for life by developing communication skills, self-discipline and respect for themselves, their peers and their world. Schools offer a broad curriculum in the key learning areas such as English, mathematics, studies of society and the environment, science, arts, Languages Other Than English (LOTE), technology, health and physical education. They also believe strongly in the benefits of a rounded education such as teamwork, self-expression and personal development that happens outside the classroom.
In Australia, students will enjoy an open and multicultural learning environment that is as personally enriching as it is educational, and develop the skills and qualities needed in the future.

High Standard of Learning
Australian schools are among the finest in the world. According to the World Population Review, Australia is in the top 6 among the world’s best countries for educationVisit SourceThese are a few things which makes education in Australia very valuable:
- Small class sizes (a maximum of 30 students in a class)
- University-trained and qualified teachers and specialist teachers in subject areas.
- Facilities of a high standard – including a high level of technology, with all schools having computers and internet access.
- ‘Gifted and talented’ programs to extend students who are high achievers.
- ‘High Achievement’ programs, which see the top students studying university-level subjects for advance credit
- Quality assurance frameworks where schools must meet required standards.
Support for School Students
Australian schools offer a strong welfare structure to ensure the ongoing support of every student such as:
- International student coordinators
- Student welfare team
- Year advisers
- School counsellors
- Careers advisers to assist students with planning and applying for post-secondary study
- English as a second language support staff and programs
- Students learn with local Australian students
- Accommodation in homestays: all host families must have a police check to meet requirements of child protection legislation and homes must meet required standards; students have a 24 hour emergency contact number.


National Curriculum and Assessment
Australia has a National Curriculum for schools developed by the Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority (ACARA). Under the National Curriculum, some periodic assessment are compulsory for students:
The National Assessment Program – Literacy and Numeracy (NAPLAN) is an annual assessment for students in Years 3, 5, 7 and 9. The assessments are undertaken nationwide, every year, in the second week in May. NAPLAN tests the sorts of skills that are essential for every child to progress through school and life. It comprises tests in four areas (or ‘domains’): reading, writing, language conventions (spelling, grammar and punctuation), and numeracy. In 2016, the NAPLAN results showed that almost 94% of children have met national minimum standards for their age.
source: https://www.nap.edu.au/naplan
Other Information
School qualifications
After a successful completion of senior secondary school (Years 11 and 12) students will receive an official certificate of qualification. The certificate will be recognised by all Australian universities, higher education and vocational education and training institutions, as well as many institutions internationally.
English as The Official Language
English is the official language of Australia and hence, the main language of instruction in schools. There may be some bilingual programs offered in some schools.
Academic Year
The Australian academic year typically begins in late January or early February and runs to mid-December. In general, Australian schools have 3 or 4 terms a year, but some states or territories have flexibility about the school year to allow for specific community contexts.

